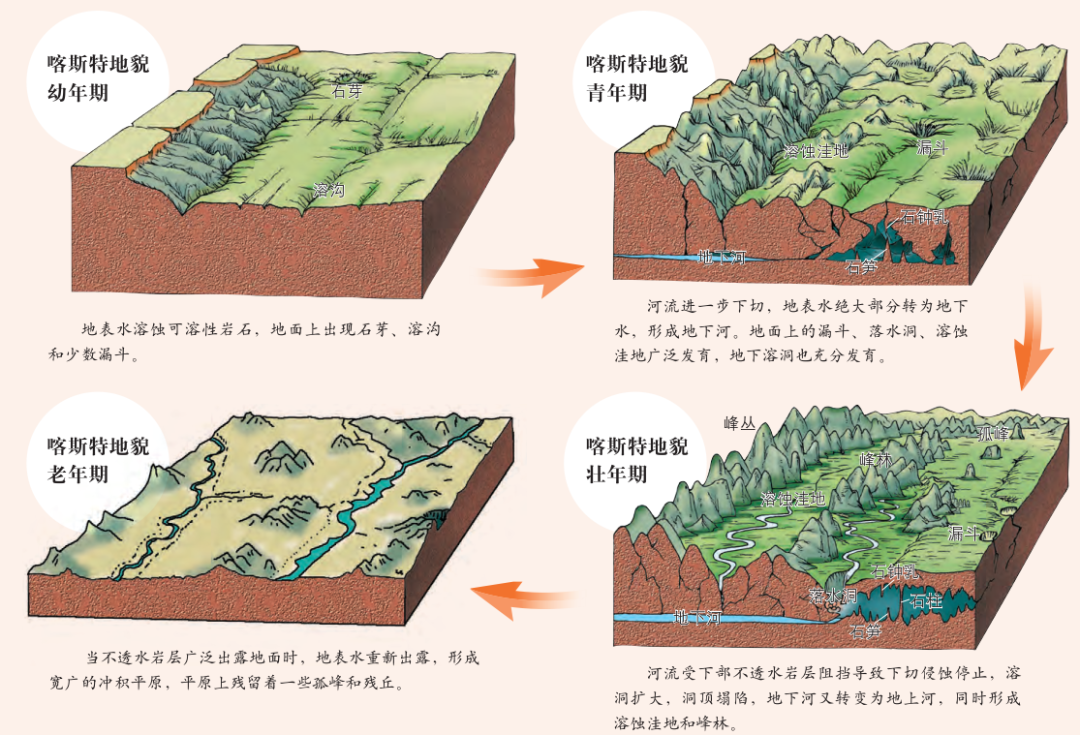
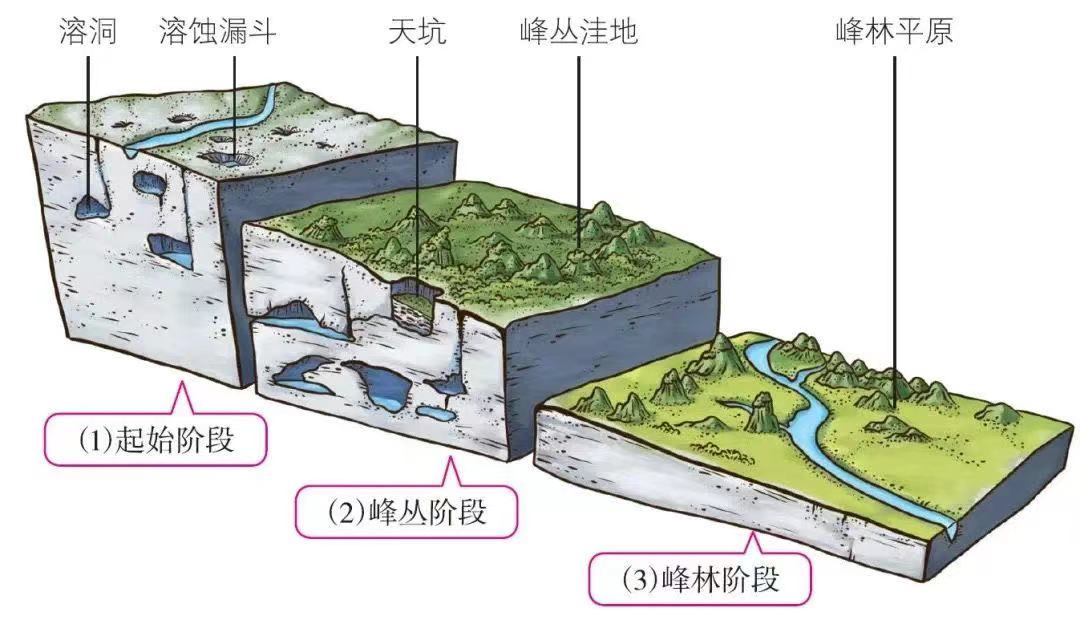
Karst Plateau landform is the general name of the surface and underground forms formed by the dissolution of soluble rocks (mostly limestone) by water with dissolution, which is also called karst landform.
The action of water on soluble rocks is generally called Karst Plateau action. It mainly involves dissolution, and also includes mechanical erosion processes such as water erosion, subsurface erosion, and collapse. This effect and the phenomenon it produces are collectively referred to as Karst Plateau.
The Karst Plateau is the name given to the carbonate rock plateau in northwestern Istria, Yugoslavia. It is known locally as Kras, which means the place where the rock is exposed. Modern Karst Plateau research originated in this place and got its name.
Karst Plateau landform is distributed in soluble rock areas around the world. There are three types of soluble rocks:
① Carbonate rocks (limestone, dolomite, Marl, etc.).
② Sulfate rocks (gypsum, Anhydrite and mirabilite).
③ Halogenated rocks (potassium, sodium, magnesium salt rocks, etc.).